Introduction
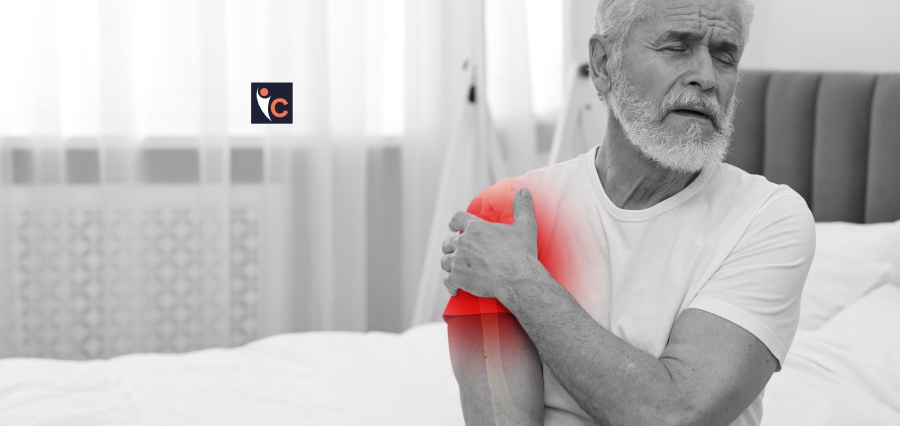
Shoulder muscle strain, a common injury, can happen at any age and regardless of activity level. It occurs when fibers in muscles or tendons overstretch or tear, resulting in difficulty in movement associated with acute or chronic pain (1) This article discusses the causes of shoulder muscle strains, their symptoms, and effective treatment regimens.
Causes of Shoulder Muscle Strain (2)
1. Repetitive Arm Motions
Shoulder muscle strain, like any other sports injury, can be caused by repetitive activities, such as archery, tennis, and swimming. Musicians are also prone to shoulder muscle strains. This type of strain is often chronic.
2. Sudden Trauma
Accidents or blows to the shoulder blades can pressure shoulder muscles, causing them to tear. This causes severe pain and difficulty in motion.
3. Poor Posture
Improper body posture while sitting or working can lead to shoulder muscle strains over time.
4. Improper Warm-up or Cooling Down
Pre-exercise warm-ups and post-workout cooling-downs are essential in preventing muscle strains.
5. Age
Age is a risk factor for shoulder muscle strain due to the natural degradation of elasticity and strength of muscles and tendons with time.
Symptoms of Shoulder Muscle Strain (3)
1. Pain
Acute or chronic pain can occur at the shoulder where muscles have been torn, ranging from mild to severe, and gets worse with motion. This pain can radiate down the arm and lead to limited mobility.
2. Swelling and Bruising
In severe cases of shoulder muscle strains, inflammation, and cellular damage may occur, representing a swollen and bruised shoulder.
3. Muscle Weakness
Muscle fatigue is possible due to strain, loss of strength, and tissue damage.
4. Limited Ability of Movement
Pain, swelling, and muscle fatigue can affect the efficacy of performing daily life activities. The limitation of the ability to move depends on the severity of the muscle injury.
Effective Treatment Options (4)
Treatment of shoulder muscle strains is essential for relief, managing cases of inflammation and tissue damage, ensuring proper and quick recovery, and preventing recurrence. Treatment options include the following:
1. The R.I.C.E Method
R: Rest – Rest the injured area and avoid using it for up to three days.
I: Ice – Apply ice for 20 minutes to reduce swelling.
C: Compression – Compress the area with a firm elastic bandage.
E: Elevation – Elevate the area above the heart level.
2. Medications
Mild pain can be relieved with over-the-counter (OTC) non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen. Stronger medications can be prescribed for severe cases, such as steroid injections and more potent painkillers.
3. Physiotherapy
Proper physiotherapy approaches help restore strength, elasticity, and flexibility. Exercises focus on stretching and enhancing muscle performance. This is a suitable treatment option for sustainable recovery.
4. Surgery
In severe cases, surgical interventions can be the most appropriate management approach, such as arthroscopic or open tendon or ligament repair surgery and shoulder replacement surgery.
5. Gradual Return to Activity
Injured patients should gradually return to sports and exercise to avoid re-injury. They should also increase the intensity of activities slowly and cautiously with the help of healthcare providers.
References
- https://nyulangone.org/conditions/shoulder-sprains-strains#:~:text=A%20shoulder%20sprain%20occurs%20when,cause%20acute%20or%20chronic%20pain.
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/shoulder-sprains
- https://www.mercy.com/health-care-services/orthopedics-sports-medicine-spine/specialties/shoulder-upper-arm/conditions/shoulder-sprain-strain
- https://www.sportspainmanagementnyc.com/shoulder-sprain-strain/
Read More: Click Here