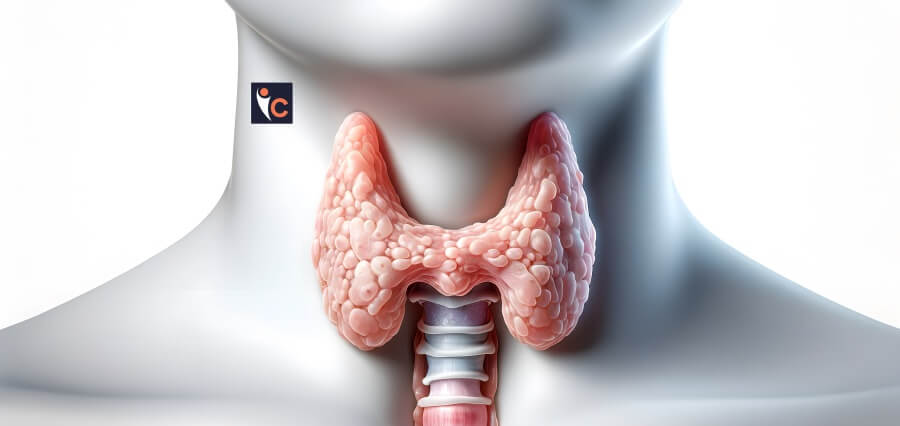
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, is responsible for regulating the body’s metabolism, temperature, and heart rate. Hyperthyroidism, also known as overactive thyroid, occurs when it produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones; triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Causes may include various medical conditions, such as Graves’ disease, thyroiditis, and thyroid nodules. (1)
Early detection and recognition of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism are essential for optimal treatment. While symptoms may vary in intensity, it is important to understand the hallmark signs. These include the following:
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms (2,3,4,5)
1. Unexpected Weight Loss:
Despite how much food is consumed, patients with hyperthyroidism experience rapid and unexplained weight loss. It is one of the primary symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
This occurs due to the elevated production of thyroid hormones, which boosts the metabolic rate, leading to weight loss.
2. Increased Appetite:
Hyperthyroidism also increases appetite, and patients feel hungry all the time, despite the weight loss. Changes in weight and appetite patterns are key indicators for recognizing the symptoms of an overactive thyroid.
3. Rapid Heart Rate:
Thyroid hormones may affect the heartbeat, rhythm, and speed, causing tachycardia, which is a rapid or irregular heart rate. If this symptom persists, a medical health professional should be consulted to evaluate the thyroid gland and start appropriate treatment.
4. Tremors
The overstimulation of the nervous system caused by hyperthyroidism may lead to fine tremors in the hands or fingers. This symptom may be bothersome for patients, especially when performing daily activities, eventually affecting quality of life.
5. Heat Intolerance
As a result of an elevated metabolic rate and perspiration, patients may become highly sensitive to heat. They may feel hot and sweaty, even in cool conditions.
6. Fatigue and Muscle Weakness
Patients with hyperthyroidism may experience significant fatigue and weakness in the upper arm and thigh muscles, affecting daily activities. These symptoms occur due to the breakdown of proteins as the body manages the overactive thyroid.
7. Changes in Bowel Movements
Patients may suffer from diarrhea, frequent bowel movements, and abdominal cramps due to elevated metabolism, which affects the gastrointestinal tract. However, other digestive conditions with similar symptoms must be ruled out.
8. Insomnia
The elevated metabolism, increased nervous system activity, and changes in body temperature can also cause difficulty sleeping. Patients may be prescribed medications to help manage this symptom.
9. Depression
Hyperthyroidism can also impact mental health, causing symptoms of depression, such as anxiety, mood swings, and reduced energy. These symptoms are caused by Increased thyroid hormone production and imbalance.
10. Goiter
In severe cases, a goiter may develop, which is characterized by the swelling and enlargement of the thyroid gland, that becomes visible at the base of the neck. A goiter is often associated with other symptoms, such as throat tightness, coughing, and trouble breathing or swallowing.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as unexplained weight loss, increased appetite, and tachycardia, early is crucial for medical evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment. Early detection enhances patient outcomes and quality of life. It also prevents long-term complications associated with this condition.
References
- https://medlineplus.gov/hyperthyroidism.html
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/hyperthyroidism#symptoms
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/overactive-thyroid-hyperthyroidism/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14129-hyperthyroidism
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/hyperthyroidism-and-depression#hyperthyroidism-and-depression
Read More: Click Here