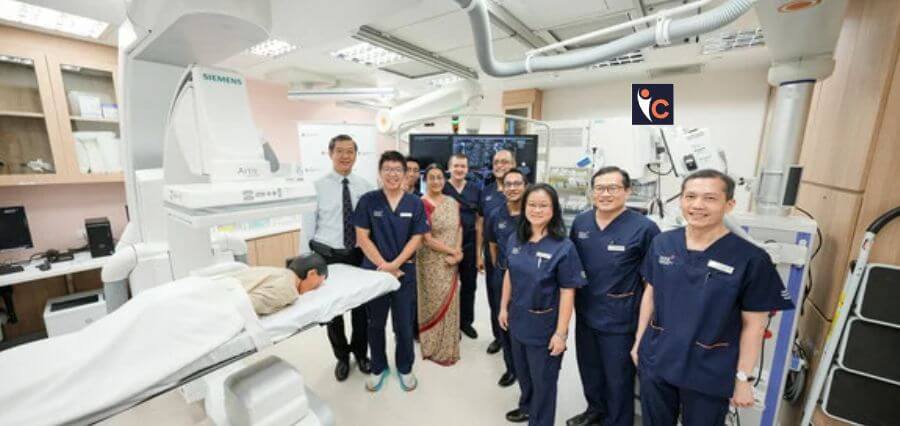
In Singapore, the National University Hospital (NUH) is undertaking a significant endeavour to establish the National University Centre for Digestive Health, scheduled for completion in the first half of 2025. Envisioned as the premier academic hub for digestive health in the region, the Centre will lead the way in research, innovations, and clinical practices, with a heightened emphasis on enhancing standards in early disease detection, accurate diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of digestive illnesses.
By incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and cutting-edge technology, the upcoming Centre will function as a comprehensive, all-encompassing hub for gastroenterology and hepatology services. It will address the increasing demands of patients with conditions related to the stomach, colon, and liver, including various cancers.
In Singapore, gastrointestinal cancers and liver cancer are prominent contributors to cancer-related mortality. According to the Singapore Cancer Registry Annual Report 2021, gastrointestinal cancers accounted for one-third of male cancer cases and roughly one-fifth of female cases.
Presently, the Centre stands as the sole establishment in Singapore implementing three AI-enabled systems: Computer-assisted detection (CADe), Computer-assisted diagnosis (CADx), and Computer-assisted quality control (CAQ). These systems operate collaboratively to enhance the identification of early gastrointestinal lesions and facilitate real-time cancer diagnosis. This advancement can result in timelier treatments or follow-up interventions for patients diagnosed with high-risk lesions, potentially enhancing prognosis and treatment efficacy.
Gastrointestinal cancers encompass malignancies affecting the digestive system, including the oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, colon, and rectum. They rank among the most prevalent cancer types worldwide, with significant morbidity and mortality rates. Risk factors vary but commonly include smoking, obesity, alcohol consumption, and dietary factors. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, unintended weight loss, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Early detection through screening programs and diagnostic techniques such as endoscopy and imaging modalities is crucial for favourable outcomes. Treatment options depend on cancer type, stage, and individual patient factors, often involving surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies.
Read More: Click Here