Breast cancer breakthrough as scientists work out how to kill ‘hibernating’ tumour cells
Scientists have made a breakthrough in breast cancer research by discovering how to eliminate ‘hibernating’ tumor cells.
This opens up new therapy options to prevent cancer from recurring. It provides new hope for individuals with oestrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer, which grows in response to the hormone oestrogen. ER+ accounts for 80% of all breast cancers, with 55,500 instances detected annually in the UK.
Luca Magnani, professor of epigenetic plasticity at the institute, said: “After surgery to remove primary oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer, patients are given five to 10 years of hormone therapy which aims to kill any remaining cancer cells. “We know that this doesn’t work for all patients though, as their breast cancer can return years, or even decades later.
“We wanted to better understand why breast cancer does return so we can hopefully find ways to stop it – so people don’t have to live in fear or face the devastating news of a relapse.”
Researchers understand that breast cancer cells can “hibernate” and avoid therapy before “waking up” years later and generating disease that is more difficult to treat.
Prof. Magnani said further “Our research identified a key mechanism used by cancer cells to evade therapy by remaining in a dormant state, hibernating before they ‘wake up’ years later and begin to rapidly divide again.”
Researchers investigated the role of an enzyme called G9a in their study, which was published in the journal Cancer Discovery. They discovered that blocking G9a prevented cancer cells from going dormant and destroyed those that were already in hibernation.
Dr Tayyaba Jiwani, science engagement manager at Cancer Research UK – which funded the research, said: “Breast cancer survival has doubled in the UK over the last 50 years thanks to better detection and screening, but there are still more than 11,000 deaths from this type of cancer every year.
“Our research has made it increasingly clear that cancer cells can lie dormant in the body for many years before being triggered to reawaken, causing cancer to return.“This study uses an innovative approach to analyse the genetics of these dormant cells and gain important insight into the mechanisms leading to dormancy.“Although at an early stage, the findings reveal potential new targets for the development of innovative treatments that prevent breast cancer from coming back.”
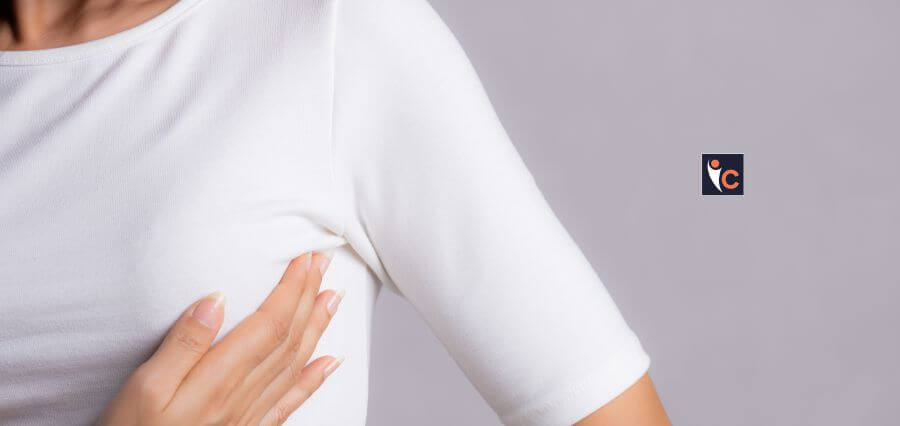
How to Check Your Breasts
There is a five-step self-exam you can perform at home to detect any changes.
Step one: Face the mirror with your arms on your hips and your shoulders straight. Look for dimpling, puckering, bulging skin, redness, pain, a rash, or changes to the nipple.
Step two: While staring in the mirror, raise both arms over your head and check for the same changes.
Step three: Keep your arms over your head and check for any fluid flowing from your nipples. This may contain milky, yellow, or watery fluids, as well as blood.
Step 4: While lying down, use your opposite hand to inspect each breast. Use a few fingers, keeping them flat and together, to make a slight circular motion around your breasts. Feel the entire breast by travelling from top to bottom in these little circles. It helps to create a strategy or pattern to ensure that every inch is covered. Apply mild pressure to the skin and tissue just beneath, medium pressure to the tissue in the center of your breasts, and hard pressure to the tissue in the back, down to your ribcage.
Step five: Feel your breasts while standing or sitting, making the same little circular motions.
Read More: Click Here