Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) was first successfully done by Handyside and since then has evolved leaps and bounds. It is a technique with the help of which we can identify genetic defects in embryos created using in vitro fertilization (IVF) prior to implantation and comprises of two components Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis(PGD) and Preimplantation Genetic Screening(PGS) now coined again as Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy(PGT-A).
Pregenetic testing for diagnosis can be done for a Monogenic (single gene disorder) or for structural rearrangement.
Preimplantation genetic testing for a monogenic (single-gene) disorder (PGT-M) – The aim of PGT-M is to achieve a pregnancy which is unaffected by a particular genetic condition, such as any known heritable genetic mutation carried by one or both biological parents. It may also be used to select embryos which have a specific genetic makeup like a compatible human leukocyte antigen complex.
Preimplantation genetic testing for structural rearrangements (PGT-SR) – The aim of PGT-SR is to achieve a pregnancy which is not affected by a particular structural chromosomal abnormality like translocation in a couple with a balanced translocation, or deletion/duplication.
Only unaffected or normal(euploid) embryos are transferred into the uterus it eliminates the need for post conception aneuploidy screening and diagnostic procedures(i.e. amniocentesis and chorionic villi biopsy)which may lead to a difficult decisions of terminating the pregnancy. Invasive antenatal diagnostic procedure even carries a small risk of abortion which is eliminated with PGT conception
Who can benefit from Preimplantation Genetic Testing?
- Women of age 35 and older. That is because there is a concern about the genetic quality of their eggs.
- Women experiencing recurrent, unexplained pregnancy loss
- Women who have experienced more than one failed fertility treatment
- Those that carry sex-linked disorders – they can choose the technique of gender determination to prevent sex-linked disease
- Carriers of single gene disorders
- Couples with family history of inherited disease
- Those with chromosomal disorders
How is Preimplantation Genetic Testing Performed?
In order to perform Preimplantation genetic testing embryos must be available for testing. The patient needs to go through a regular IVF cycle in which hormones (gonadotropins) are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce more than one egg. When the follicles reach a desired size they are triggered with a HCG injection and the oocytes are then retrieved from these follicles under short general anesthesia. The procedure in done under transvaginal ultrasound guidance. Then the mature eggs (oocytes) are then injected with the partners or husbands sperms and are allowed to grow in the laboratory up until the day on which a biopsy can be taken i.e. day 3 or day 5.
During the biopsy an embryologist can either do a day 3/day 5 biopsy. In day 3 PGT they take a single cell biopsy and then send it for testing in day 5 PGT they take a biopsy of trophoectoderm (many cells) and then send it for testing.
The genetic material from these cells is then amplified using whole genome amplification (WGA) and then tested using the newer techniques of aCGH or more recently Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) which enables testing of all 24 chromosomes.
The report is then available after 7 days of sending the sample for testing if a day 5 biopsy was sent and in 2 days if a day 3 biopsy was sent allowing possibility of fresh transfer in a day 3 biospy.
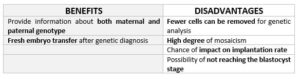
TABLE 1: Benefits and Disadvantages of Day 3 Biopsy
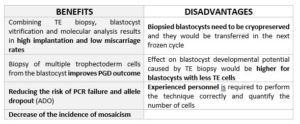
TABLE 2: Benefits and Disadvantages of day 5 Biopsy
The report can report a normal(euploid), abnormal(aneuploid) or a Mosaic embryo. In cases of Mosaic embryo a detailed genetic counseling should be done explaining the risk and the benefits of taking an embryo transfer.
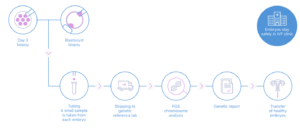
Now-a-days newer noninvasive pre-genetic testing techniques like analysis of cell free DNA in embryo culture and minimally invasive techniques like Blastocelic fluid aspiration are available
But before you opt for pregenetic testing of any kind you should know the risks and the benefits
Benefits of PGT
- Reduces the requirement for amniocentesis later in the pregnancy. Amniocentesis is prenatal testing done when the fetus is aged 10-16 weeks, where a needle is used to obtain a sample of amniotic fluid. As it is invasive and carries some risk, having an option to avoid this test may be of valuable benefit to some patients.
- Enables the implantation of only selected quality pre-embryo(s).This increases the chances of getting a pregnancy and also decreases the chance of a miscarriage.
- Decreases chance of multiple births.As they are screened for quality, embryos can be transferred are fewer. It helps to identify a single best embryo and allows a single embryo to be transferred which in turn helps avoid the risks and complication of a multiple pregnancy and birth.
Risks of PGT
- Some genetic disorders may not show up until a later stage in life. PGD is very efficient, but in rare cases a defective embryo may fail to show the disease or defect until mature.
About the Author
Dr. Ritu Hinduja, MD, MRM (UK), DRM (Germany), Fellowship in Reproductive Medicine (India, Spain, Israel), and Certificate in Genetic Counseling, is a well-known medical practitioner. She specializes in reproductive medicine and infertility treatment and has an experience of more than eight long years in it. For her dedication and contribution to the field, she has been honored with various prominent awards like Dr. Shantabai Gulabchand Travelling Fellowship Award, Dr. Pramila Bhatia-Young Scientist Award, and FOGSI Dr. Shanti Yadav Award for Infertility















