Regenerative medicine deals with the “process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function”. This field holds the promise of engineering damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body’s own repair mechanisms to functionally heal previously irreparable tissues or organs.
Regenerative medicine also includes the possibility of growing tissues and organs in the laboratory and implanting them when the body cannot heal itself.
What is Platelet Rich Plasma? (PRP)
also known as autologous conditioned plasma, is a concentrate of platelet-rich plasma protein derived from whole blood, centrifuged to remove red blood cells.
The theory behind this modality of treatment was derived from the natural healing process as the body’s first response to tissue injury is to deliver platelets to the injured area. Platelets promote healing and attract stem cells to the site of injury.
How is PRP obtained?
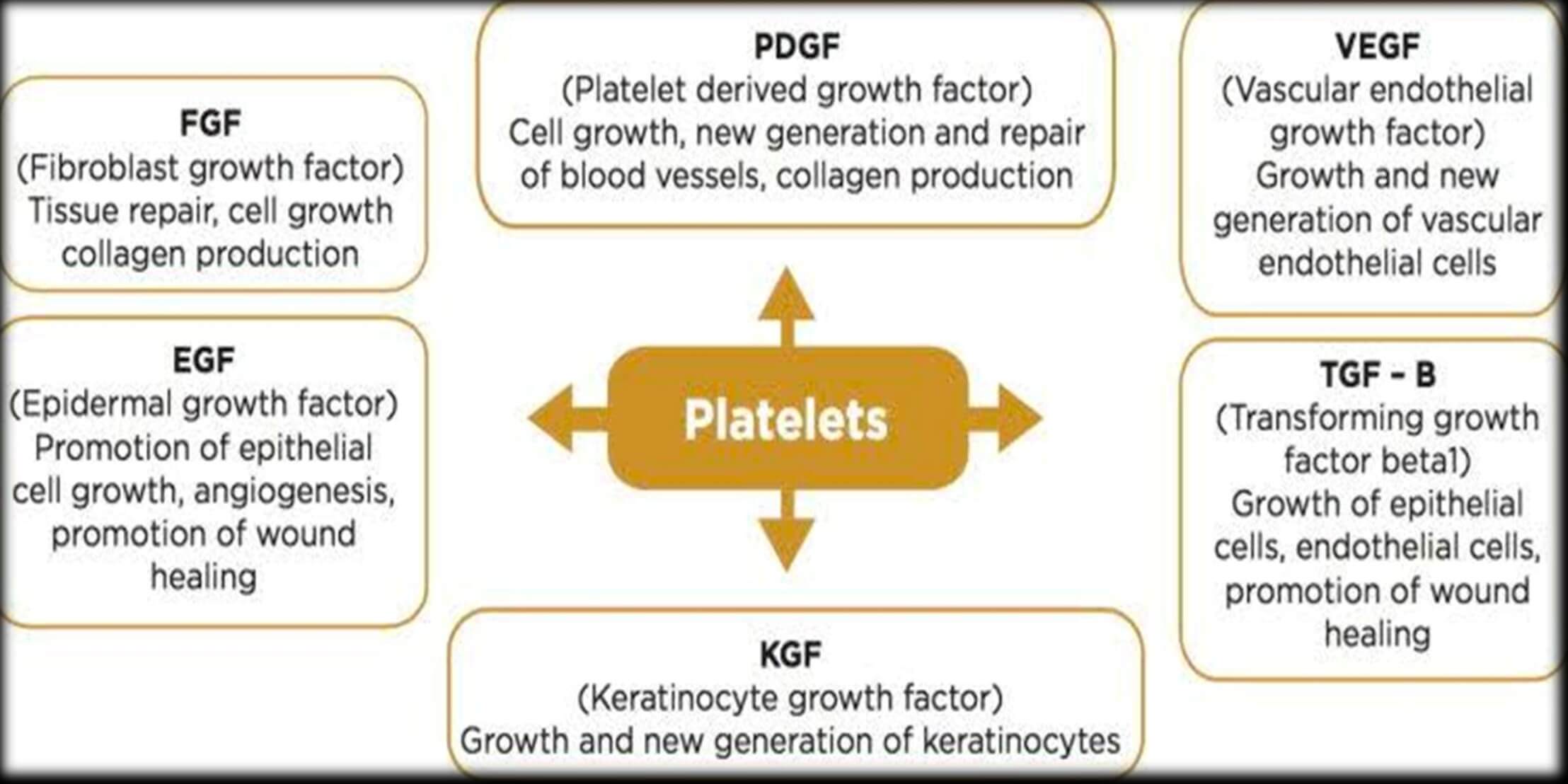
Autologous PRP is derived from whole blood of the same individual centrifuged to remove RBCs. The remaining plasma has a higher concentration of growth factors 5-10 folds greater than whole blood.
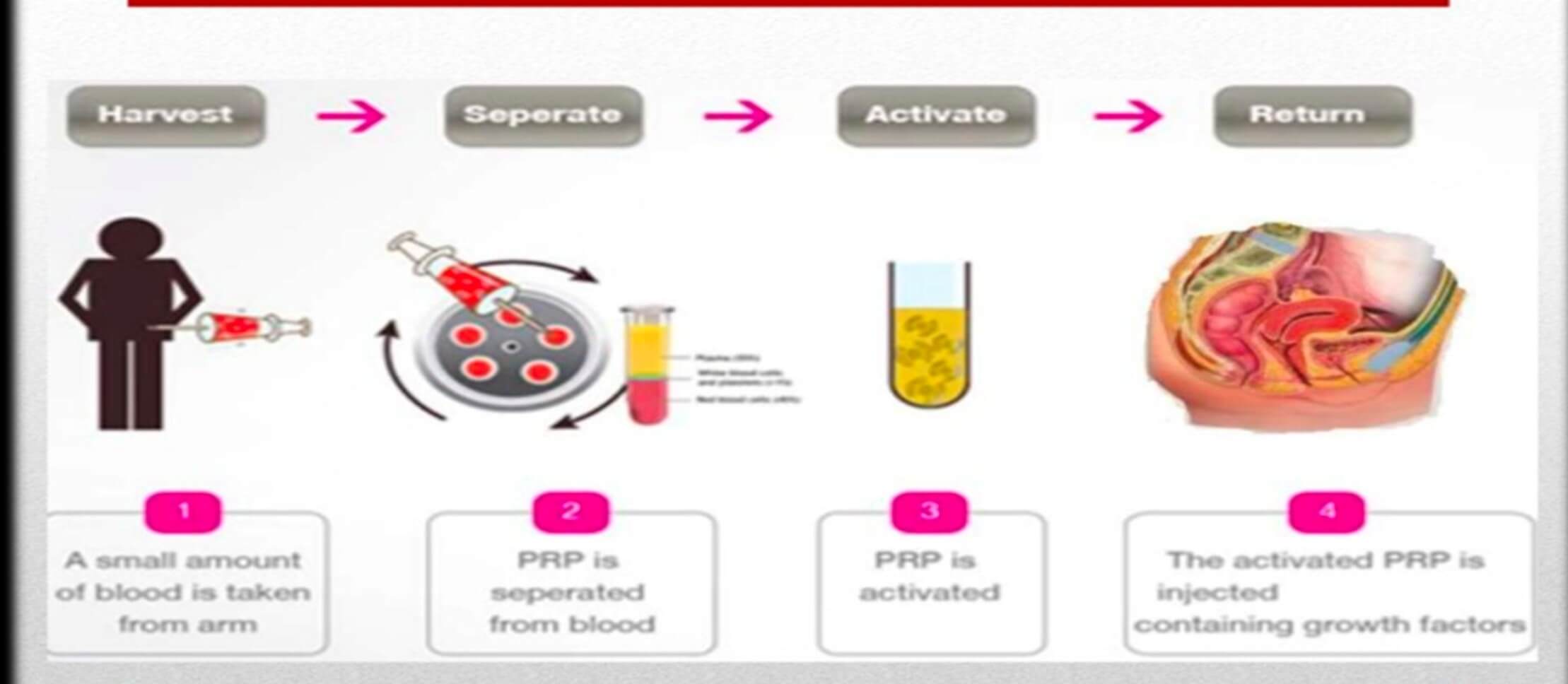
PRP is extracted using a specially designed centrifuge machine and a special conical tube.
- About 15 ml of venous blood is taken from the patient, injected into the conical tube and centrifuged. (21-24degree Celsius ) @1200 rpm for 12 minutes
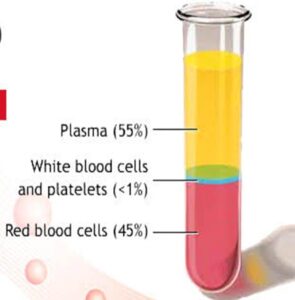
Blood separates in 3 layers :
- Upper: platelets and WBC
- middle buffy coat (rich in WBC)
- lower: RBCs.
The upper and intermediate Buffy layers are transferred to an empty sterile tube. The plasma is centrifuged again @ 3300 rpm for 7 min to help information of soft pellets at the bottom of the tube. Discard the upper 2/3 portions of plasma as this volume is PPP (Platelet Poor Plasma).
Pellets are homogenized in lower 1/3rd to create PRP ( Platelet Rich Plasma ).
30 ml of venous blood yields 3-5 ml of PRP.
Figure 1: Layers after centrifugation
Figure 2: How is PRP prepared
Figure 3: Composition of PRP
Ovarian Rejuvenation
It is believed that even after the ovarian reserve is exhausted there are still some dormant oocytes/eggs which are remaining in the ovary of the woman.
Ovarian Rejuvenation is a procedure intended to re-awake egg maturation and development within the ovary by activating dormant follicles. It is a Process by which the production of eggs is artificially stimulated, giving women the chance to produce more eggs than they would naturally have been able to, and therefore giving them the chance to conceive using their own genetic material. To do so PRP is used
How is Ovarian Rejuvenation done?
- Patient is called at the end of the periods, before the follicles begin to grow on the empty stomach
- Blood is withdrawn from the patient and PRP is obtained from it
- The PRP is injected in both the ovaries under anesthesia under the guidance of a transvaginal ultrasound
- The patient can go home after 1- 2 hours
- The procedure needs to be repeated every month for three months
- AMH , FSH, LH and Estradiol levels are measured at monthly intervals in women who do not menstruate, and during the menstrual flow in menstruating women for a period of six months
- If the AMH levels rise while the FSH, LH, and estradiol levels become lower, there is objective evidence of ovarian rejuvenation is demonstrated
Platelet rich plasma therapy for thin endometrium.
Thin endometrium is defined as an endometrium which measures less than 6 to 7 mm on transvaginal ultrasound, and remains the of the main enigmas in treatment of infertility. Intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a new approach that has been suggested for the treatment of thin endometrium .
PRP is infused in the endometrium using an IUI catheter and the endometrium is measure again after 72 hours
Infusion of PRP has shown to improve the endometrial thickness and the blood flow as well leading to better implantation rates in IVF
What are stem cells?
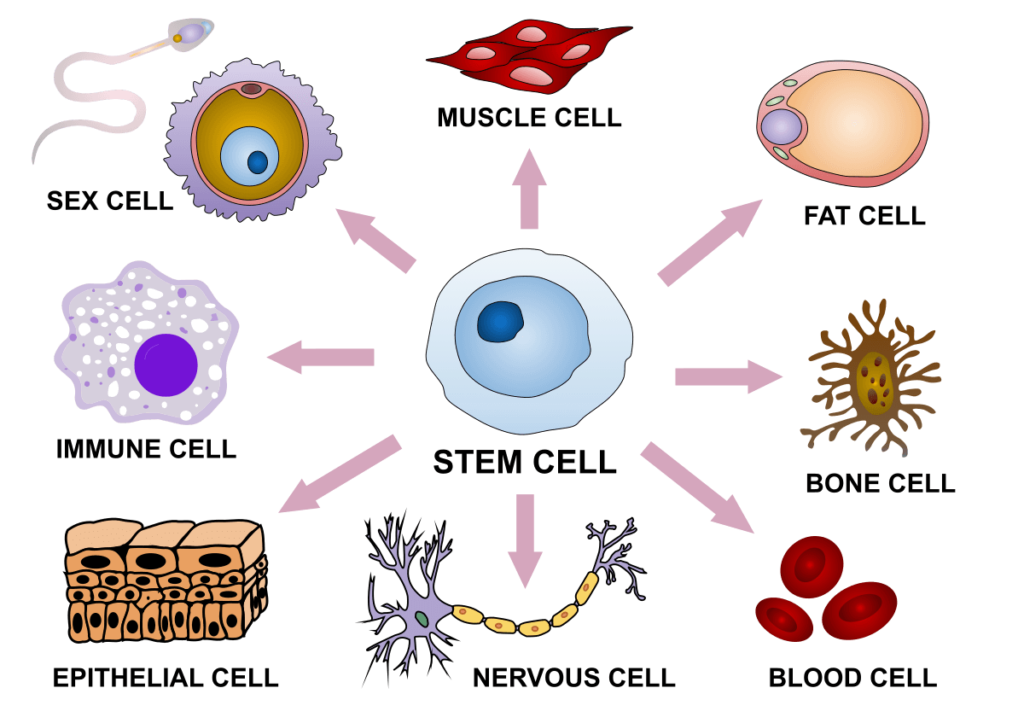
Stem cells are special human cells that have the ability to develop into many different cell types, from muscle cells to brain cells. In some cases, they also have the ability to repair damaged tissues. Due to their unlimited source and high differentiation potential, Researchers believe that stem cells can stem cells can be considered as potentially new therapeutic agents for various ailments some of them being cancer, Alzheimer’s and infertility
Types of stem cells
Stem cells are divided into two main forms: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells : are used in research and they come from unused supernumerary embryos resulting from in vitro fertilization procedure and that are donated to science. These embryonic stem cells that are obtained from embryos are pluripotent, meaning that they can turn into more than one type of cell.
Adult stem cells
Adult stem cells are of two types. One that comes from fully developed tissues, like the brain, skin, and bone marrow.In these tissues there are only small number of stem cells available and only a certain type of cells can be generated from them. For example, a stem cell derived from the liver will only generate more liver cells.
The second type which are induced pluripotent stem cells. These are adult stem cells which have been manipulated in a laboratory to make them pluripotent in nature just like that of embryonic stem cells. It was in 2006 that the Scientists first reported that human stem cells could be reprogrammed this way. Scientists have not yet found a induced pluripotent stem cell line that can develop into every kind of cell and tissue, even though induced pluripotent stem cells don’t appear to be clinically different from embryonic stem cells,
Figure 4 : Cells that can be derived from stem cells
Stem cells In Infertility
There are various causes of infertility which grieve the couple who are trying to have a child. The biggest challenges in the field of infertility are giving a biological child to women with decreased ovarian reserve and a man with no sperms (azoospermia)
Eggs and sperm have not yet been derived from human pluripotent stem cells (PSC). They have been derived from pluripotent stem cells of mouse leading to healthy, fertile pups from either PSC derived sperm or eggs.
Katsuhiko Hayashi and Mitinori Saitou ; two researchers from Japan have pioneered this technology. They were the first In 2011, to show that sperm made from male PSC enabled infertile male mice to have healthy and fertile pups. They continued their research, and in the very next year demonstrated that female PSC could be turned into eggs which could develop into healthy and fertile pups.
About the Author
Dr. Ritu Hinduja, MD, MRM (UK), DRM (Germany), Fellowship in Reproductive Medicine (India, Spain, Israel), and Certificate in Genetic Counseling, is a well-known medical practitioner. She specializes in Reproductive medicine and Infertility treatment and has an experience of more than a decade in it. For her dedication and contribution to the field, she has been honored with various prominent awards like FOGSI Chorion Award for best research,FOGSI- Kumud Tamaskar Award for best research in infertility , FOGSI- Dr Shanti Yadav Award for Infertility
MOGS – Dr. Shantabai Gulabchand Traveling Fellowship Award, Dr. Pramila Bhatia-Young Scientist Award and Dr H S Palep Award for the best research in Recurrent Pregnancy Loss.